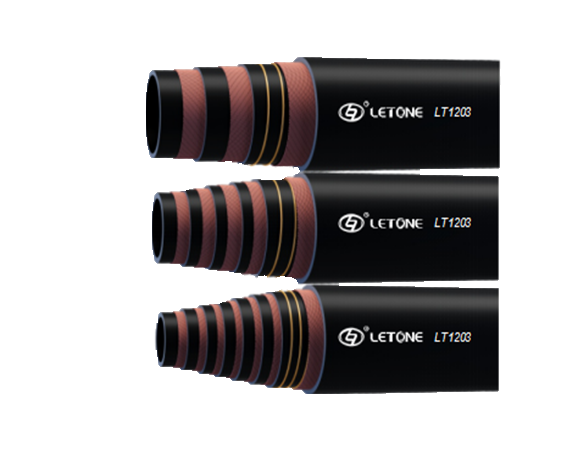
Construction Nap Hose
release date:2023-07-19 09:54:49
reading volume:
share:
Core Layer
The core layer is a high-speed backbone that optimizes communication transport within the network. Its functions include ensuring redundancy to access devices, routing to the distribution layer, route redistribution and router summarization. It interacts with the distribution layer to provide access-list maintenance and ensure quality of service and troubleshooting. The core layer also provides kink-resistance. It consists of an extruded synthetic rubber or softer plastic tube that transports water. It has a virgin water barrier on the inside that prevents it from coming into contact with recycled materials used in other layers.Reinforcement Layer
A construction nap hose's reinforcement layer resists both outward pressure from the core tube and inward force from external sources. It is a key factor in determining the burst pressure rating of a hose, and it also contributes to kink resistance. Reinforcement wires are typically made from fiber or stainless steel and come in two styles: coiled and braided. The choice of a hose's reinforcement wires is important because it can influence the hose's overall performance and longevity. For example, a coiled reinforcement is easier to manufacture but can lack the strength of its braided counterpart. Additionally, a coiled reinforcement may untwist itself when pressurized, which can result in failure. A hose with a braided reinforcement will not untwist and is more likely to withstand high pressures.Jacket Layer
The jacket is the final layer that protects the inner hose from external forces, such as abrasion. Often woven with polyester yarns that are engineered to resist abrasion, mold and mildew, the jacket helps ensure that the hose is durable enough for firefighting applications. Woven fabric jackets are soft and easy to handle, making them a favorite for firefighting professionals. Rubber jackets can be used on some hoses that require additional durability and flexibility. They provide an added level of resistance to abrasion, chemicals and oils that may damage a standard woven jacket.
Thermoplastic jackets can also be formed into specific shapes that help with routing and reduce kinking. They can also be stored in smaller boxes than traditional wooden crates, cutting shipping costs and floor space while offering greater storage versatility. Additionally, some thermoplastic hoses are extruded, which provides a stronger connection between the liner, braid and jacket. This helps prevent abrasion and ensures the hose maintains its shape under pressure.
Rubber jackets can be used on some hoses that require additional durability and flexibility. They provide an added level of resistance to abrasion, chemicals and oils that may damage a standard woven jacket.
Thermoplastic jackets can also be formed into specific shapes that help with routing and reduce kinking. They can also be stored in smaller boxes than traditional wooden crates, cutting shipping costs and floor space while offering greater storage versatility. Additionally, some thermoplastic hoses are extruded, which provides a stronger connection between the liner, braid and jacket. This helps prevent abrasion and ensures the hose maintains its shape under pressure.