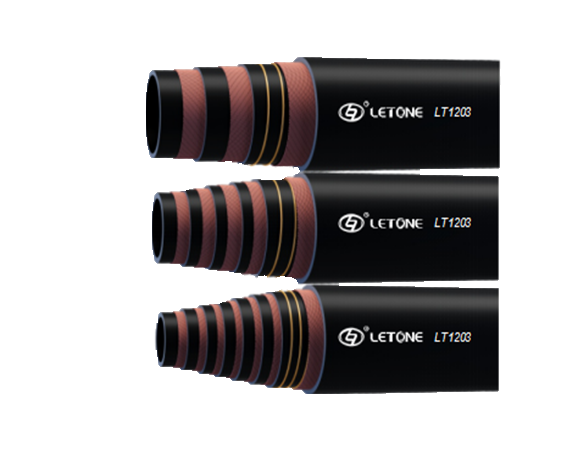
Blowout Preventer Armored Hose
release date:2023-08-14 09:35:45
reading volume:
share:
Blowout preventer (BOP) systems provide fail-safes for drilling operations. Having a system in perfect working order is vital for the safety of personnel, equipment and the environment. The control hoses used in these systems are required to withstand high pressure, heat and flame exposure. Gates BlackGold MegaShield 5000 is the perfect solution to these demanding requirements.
Flame Resistant
Fire resistant means the hose is designed to keep its working pressure in a fire situation. This is very important for BOP systems because it can keep the pressure in place and allow the rest of the system to continue operating in case of an emergency. BOP hydraulic control line hoses (API 16D) used on blow-out preventer systems are manufactured with superior components to operate withstand tough crisis oilfield conditions including fire. They are capable of containing the hose rated working pressure in a flame temperature of 1300 degF (+700 degC) for 5 minutes. They are made of multiple layers of textile fabric and steel cable with one layer middle rubber placed between the cable layers and a stainless steel armored cover to handle abrasion, corrosion, cutting, gouging, oil and weather. They also feature crimped couplings that can withstand high temperatures and abrasion. BOP hoses are available in various sizes and working pressures. These are also offered in a range of end configurations like NPT, JIC and BSPT.Corrosion Resistant
The ability to withstand corrosion is an important feature of any metal hose. Many of the alloys used in flexible metal hoses, such as Monel 400 and Hastelloy C-276, have excellent resistance to media. The wall thickness of a hose also impacts its corrosion resistance, with thicker walls having higher levels of protection from harsh environments and media. Blowout preventer hoses are used to connect the BOP and other equipment on drilling platforms. They must be able to withstand high pressure and fire exposure. Our BOP control lines meet API 16D standards and can withstand a minimum of 1300 degF (+700 degC) flame temperature at rated working pressure for five minutes.
Blowout preventer hoses are used to connect the BOP and other equipment on drilling platforms. They must be able to withstand high pressure and fire exposure. Our BOP control lines meet API 16D standards and can withstand a minimum of 1300 degF (+700 degC) flame temperature at rated working pressure for five minutes.